Antimicrobial finish on textiles using plant extracts
Various natural anti-microbial agents for application on textiles have been explored in this article.
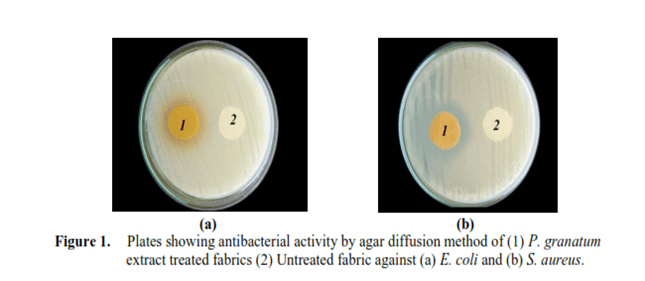
The plant extract treated fabrics were subjected to the antimicrobial activity test against the E-coli and S.aureus bacteria and also the finished samples have been analyzed for their durability of the finish by standard methods. There were no bacteria found on the surface of the treated fabrics and shows an appreciable zone of inhibition against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The combinatorial plant extracts show a very good zone of inhibition when compared to individually treated fabrics. The treated fabrics also have greater durability. The finish which is applied to the fabric did not affect any physical properties of the fabric. Since these plants are extensively available in the market, the opportunity for implementing this antimicrobial finish in the textile industry is high.
Fabrics generally carry various microorganisms which cause several problems to the wearer. The speedy growth in the textile industry has created many opportunities for a variety of innovative finishes including anti-microbial. In today’s world, naturally, renewable resources are increasingly being required as a result of human dedication to protecting the environment.
Apart from new innovations created using the fabric, value-added finishing gives add up value to the fabric in this situation. During the finishing process, the fabric attains beneficial characteristics like resistance to fire, wrinkle, mildew, etc. These high value-added fabrics have generated a demanding consumer market. In the last few years, there is a growing awareness about the healthy and hygienic surrounding condition.
The diseases normally spread from person to person and through the surface touch of the hands, clothes, etc. of that infected person. Antimicrobial fabrics have its large acceptance as surgical clothes, undergarments, baby clothing, etc. The antimicrobial finishing treatment is now extended to the traditional clothing and the home textiles. The antimicrobial agents kill or inhibit the growth of pathogens to control their effect.
The natural fibres like cotton get easily attacked by the microbes, because of the presence of carbohydrates in the fibre. Antimicrobial finished fabrics have a wide variety of applications in sports clothing, Footwear, medical textiles, furniture, automotive textiles, intimate apparels, etc.
The presence of a microorganism in the fabric causes an unpleasant odour, staining and also causes health problems. Microbial infections cause some danger to the skin and therefore, the garment which is worn next to the skin requires an antimicrobial finish. To protect the skin of the wearer, the application of antimicrobial finish using some herbs are done.
Antimicrobial agents are of two types: leaching and non-leaching. The synthetic antimicrobial agents such as quaternary ammonium compound, triclosan and many others are used for the antimicrobial finish. However, these synthetic antimicrobial agents are durable but they cause many side effects. Currently, the synthetic antimicrobial agents are banned according to the US and European standards, there is an increasing demand for eco-friendly antimicrobial textiles depend on natural antimicrobial agent such as chitosan which does not cause any harm to the wearer.
There are a various variety of herbs which are widely used as a traditional medicine in America, Africa, Europe, etc. for treating various type of diseases. The different parts from the organic plant such as papaya, aloe vera, neem, banana, hemp extracts can also be used for the purpose of antimicrobial finish. Many plants in the world contain the compound which is responsible for the antimicrobial activity. There are various compounds in the plant which is responsible for the antibacterial activity such as tannin, flavonoids, terpenoids, etc. They are both bacteriocides (which kills the micro-organism) and bacteriostatic (which inhibit the growth of micro-organism).


(a) 10% Aloe Gel (b) 10 % Neem and (c) 5% Aloe Gel and 5% Neem
Environment-friendly antimicrobial textile can be produced by the use of plant extracts. Various plants have been gathered and they are tested for their antimicrobial activity. An effective study was regulated to evaluate the plant extracts both qualitatively (AATCC-147) and quantitatively (AATCC-100) for their antimicrobial activity. Although the plant extracts have shown effective antimicrobial activity, the vital issue is the wash durability. The durability of antimicrobial finishing against washing was assessed using quantitative (ICP-OES) and semi-quantitative (LA-ICP-TOF-MS) methods. The physical properties (weight, thickness, fabric structure, count, EPI and PPI) of the fabric before and after application of finish have also been analysed. There are various natural antimicrobial agents available, but limited studies have been carried out for their antimicrobial activity on the textile materials.


