Non-Woven Fabrics
Non-woven, origin, properties, and application
Nonwovens do not depend on the interlacing of yarn for internal cohesion. Intrinsically they have neither an organized geometrical structure. They are essentially the result of the relationship between one single fiber and another. This provides nonwoven fabrics with characteristics of their own, with new or better properties (absorption, filtration) and therefore opens them up to other applications.
Absorbent hygiene products
Modern disposable absorbent hygiene products (AHPs) have made an important contribution to the quality of life and skin health of millions of people. Users of AHPs (i.e. baby diapers, feminine hygiene products and adult incontinence products) benefit from the softness, smoothness, leakage prevention, strength and protection provided by nonwoven fabrics.

Typical feminine hygiene product composition


Typical tampon composition

Typical incontinence product composition

Nonwovens are used in baby diapers, feminine hygiene products, and incontinence products as:
- The top sheet or cover-stock
- Leg cuff
- Acquisition/distribution layer
- Core wrap
- Back sheet
- Stretch ears
- Landing zone
- Dusting layer
- Fastening systems
The advantages of using nonwovens instead of traditional textiles
- Excellent absorption
- Softness
- Smoothness
- Stretch-ability
- Comfort and fit
- Strength
- The double fluid barrier effect allows moisture to be absorbed and retained
- Good uniformity
- High strength and elasticity
- Good strike-through wet back, and run off
- Cost-effectiveness
- Stability and tear resistance
- Opacity/stain hiding power
- High breathability
Main technologies used
- Air-laid
- Carded nonwovens
- Spun melt
- SMS
- Spun bond
Other components of absorbent hygiene products
- Fluff pulp
- Superabsorbent Polymers
- Impervious backing films
- Adhesive
- Elastics
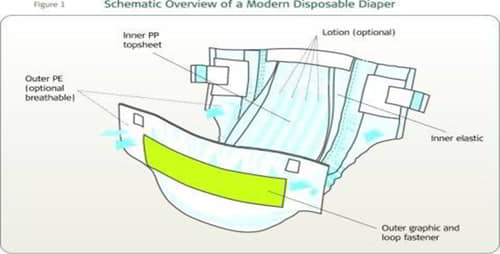
Most disposable diapers are made with the following basic components
Polyethylene or cloth-like film
This is used as the back sheet, that prevents the liquids from leaking out of the diaper. The back-sheet can also be given a cloth-like look, by adding a thin polypropylene non-woven sheet to the film, using either the hot-melt process or the heat and pressure method with direct extrusion to the nonwoven. Contrary to popular belief, the cloth-like back sheet is not cloth -it is made of plastics. Breathable cloth-like material can also be used instead of the film.
Not many know that even a breathable diaper with 200 ml of urine loses less than 2.5% of its weight over a period of 24 hours and this evaporation is enough the cool the diaper, which may not be as comfortable at night. For more information about “breathability” please use this link: breathable diapers.
Tissue
A special tissue paper that is different from the regular bathroom tissue and has higher elasticity and wet strength is another important component of a diaper. The tissue essentially serves as a carrier for the pad (the pad is the absorbent core of the diaper) and helps reduce the pin holes created during the compression process carried out by continuous drum forming systems. This tissue, typically at 16 grams/m2 (also abbreviated as GSM) or more, protects the inner plastic from superabsorbent particles.
Instead of tissue, it is possible to use a low gage SMS nonwoven material as the carrier (for the pad), it can be placed right next to the back sheet or as a full wrap material around the core. In order for the SMS carrier to be cost-competitive against tissue paper, it needs to be less than 12 GSM.
Hot Melts
They are used to glue the different components of the diaper, such as the pad and the elastics. They are made of a mixture of resins, oils, and tackifiers. The hot melt adhesive is applied in molten form and when it cools down it provides the required bonding force to glue the materials. Most of the time two types of adhesives are used: a construction adhesive, for the back sheet and the nonwovens, and an elastomeric adhesive, for the leg and waist foam elastics.

The elastomeric adhesive has higher elasticity and bonding strength and is generally more expensive than construction adhesives. When the diaper pad is very thin, another specialty adhesive is known as “pad integrity adhesive” is also used to add strength to the diaper core when it is wet. This integrity adhesive is especially useful when SAP loadings exceed 25% of the total pad weight -i.e. when the weight of the SAP is more than a quarter of the weight of the pad. For a list of hot melt, suppliers follow this link: Hot Melts.
Hydrophobic Non-woven
It is used as a top sheet for the leg cuffs; it prevents water from passing through. It is made of polypropylene resin without any added surface surfactants. The hydrophobic nonwoven prevents leakage out of diapers. By applying a surfactant to a restricted area, it is possible to make a roll of hydrophobic nonwoven only partially public. This is known as the Zebra process and it is an important feature designed to avoid leakage during leg cuff construction. For nonwoven suppliers use this link: Nonwovens.
Hydrophilic Non-woven
It is the main top sheet, the top surface that is in contact with the baby’s skin. It allows the liquids to flow into the diaper core. The difference between the two non-woven (philic and phobic) is the surfactant treatment used in the process. The surfactant treatment reduces the surface tension of the nonwoven, reduces the contact angle with the liquid, and allows it to pass. Flow dynamics within the diaper core prevent liquids from returning to the surface. Most nonwovens used in diapers are made with the spun bonding process, though it is possible to use thermally bonded nonwovens also, which are softer but have lower resistance and strength. Trough Air Bonded nonwovens which are loftier, can also be used. For nonwoven suppliers use this link: Nonwovens.
Elastics
Used to improve the fit of the diaper, usually made of polyurethane or polyester foam, synthetic rubber or Lycra® (also known with the generic name Spandex). They are used in cuffs, for the waist and the legs; they can also be used as lateral side panels and in tape construction. Most gasketing cuffs use spandex to provide a seal with the baby’s legs. Spandex can stretch as much as 400% of its original length before it breaks, however it is typically used at less than 300% stretch. New generations of softer and stronger elastic materials are reportedly in the pipeline. For a list of suppliers use this link: Elastomerics.

Lateral Tapes
In premium diapers, VelcroR type materials have been used to provide mechanical grip, it is also known as the “hook tape”. In lower-priced diapers, adhesive tapes made of polypropylene are used. Then there are new versions of elasticized Nonwoven Velcro Tapes. In a few years, baby diapers may replace training pants with the help of these new stretchable fastening systems that offer the same characteristics to the consumer but cost less. Some adult diapers use what is called the “target tape” system, where the tape has two adhesive tabs to avoid the need for frontal tape. This is a cheaper alternative for adult diapers but not as good as the one using frontal tape which does not require repositioning of the tape on top of the target. For a list of suppliers use this link: Tapes and Closure systems.

Frontal Tapes
This is used to facilitate multiple repositioning of the lateral tape without tearing the back-sheet, it is made of polypropylene film and attached to the front of the diaper with adhesive. Its use has helped to reduce the thickness of the poly film without the risk of potential tears associated with the opening of the lateral tapes from the back sheet. In premium diapers, a special loop system has been developed in order to use Velcro-type fasteners (also called the “hook and loop” system). This loop tape can use a “locked loop” or a “brushed loop” in order to provide a softer texture or a stronger grip.
A new generation of nonwoven materials expected to be commercialized in a few years may eliminate the need for frontal tapes – the whole backsheet will be used to reposition mechanical tapes. The frontal tape can have a printed design that can be random or synchronized; some patents may protect the use of synchronized printing in some markets. Tapes and Closure systems.
![]()
Cellulose
Used in the construction of the pad, it gives integrity and absorbing capacity to the diaper. The capacity of normal cellulose pulp is around 10 cc of water per gram of pulp when the diaper is in “free swell” but less than 2 cc when subjected to 5 KPa of pressure; that is why a superabsorbent material is also needed to hold the liquids under pressure. Cellulose comes from pine trees, generally obtained from well-managed forests. Liquids are absorbed by the capillaries in the void spaces between the fibers and the surface tension angle between the fibers and the water.
The typical fiber length used in diapers is about 2.6 mm. An alternative to the pulp is to use air-laid synthetic fibers. However, it is still difficult for air-laid synthetics to compete with pulp unless it is a niche market product and thickness is more important for the consumer (as in the case of some sanitary napkins and the adult diapers used by active people) than the cost. Cellulose acetate, the material used to make cigarette filters, has been used in some absorbent products. A PP synthetic fiber has also been attempted for absorbent core formation. For a list of pulp, suppliers use this link: Fluff Pulp.
Acquisition and Distribution Layer
Also known by its abbreviation ADL, it is a sub-layer used between the top sheet and the absorbent core. Sometimes used in full length but mostly preferred as a patch near the target zone where urine is most likely to be deposited. This sub-layer is especially needed when the absorbent core is very thin -the sub-layer quickly moves liquids into the absorbent core and reduces potential leakage. The ADL is very important to provide a sense of dryness to the skin, providing additional separation between the wet pad and the skin.
ADL’s should be used whenever the mix of SAP in the absorbent core exceeds about 15% by weight or when the liquid penetration time requires a boost in order to avoid diaper leakage due to liquid accumulation inside the diaper. ADL’s are made either of through air bond (TAB) nonwovens, “curly” fibers such as in P&G’s pampers and some Ontex diapers, or some kind of “high loft” nonwoven. An aperture film, made of perforated plastic film, has also been used successfully in some markets. Lower priced diapers sometimes use resin-bonded nonwovens, but they do not work as well. For acquisition, nonwoven suppliers use this link: Nonwovens.

Sodium Polyacrylate
Also known as super-absorbent or “SAP” (super absorbent polymer), Kimberly Clark used to call it SAM (super absorbent material). It is typically used in fine granular form (like table salt). It helps improve capacity for better retention in a disposable diaper, allowing the product to be thinner with improved performance and less usage of pine fluff pulp. The molecular structure of the poly-acrylate has sodium carboxylate groups hanging off the main chain.
When it comes in contact with water, the sodium detaches itself, leaving only carboxyl ions. Being negatively charged, these ions repel one another so that the polymer unwinds and absorbs water, which is attracted by the sodium atoms. The polymer also has cross-links, which effectively leads to a three-dimensional structure. It has a high molecular weight of more than a million; thus, instead of getting dissolved, it solidifies into a gel.
The Hydrogen in the water (H-O-H) is trapped by the acrylate due to the atomic bonds associated with the polarity forces between the atoms. Electrolytes in the liquid, such as salt minerals (urine contains 0.9% of minerals), reduce polarity, thereby affecting superabsorbent properties, especially with regard to the superabsorbent capacity for liquid retention. This is the main reason why diapers containing SAP should never be tested with plain water. Linear molecular configurations have less total capacity than non-linear molecules but, on the other hand, retention of liquid in a linear molecule is higher than in a non-linear molecule, due to improved polarity. For a list of SAP suppliers, please use this link: SAP
Example of a linear molecule

The superabsorbent can be designed to absorb higher amounts of liquids (with less retention) or very high retentions (but with lower capacity). In addition, a surface cross linker can be added to the superabsorbent particle to help it move liquids while it is saturated. This helps avoid the formation of “gel blocks”, the phenomenon that describes the impossibility of moving liquids once an SAP particle gets saturated.
Top Sheet surface add-on lotions
In order to create novelties for product differentiation, several topical lotions are added to the nonwoven top sheet, among others: Aloe Vera, Vitamin E, Petrolatum, Almond Oil, Vitamin D, Oat Extract, Jojoba, etc. There is another trend to use antibacterial lotions (such as tertiary ammonia or silver salt compounds); however, many pediatricians are against its use for obvious reasons.
Decorated Films and wetness indicators
For even greater product differentiation, some diapers use decorated films underneath the cloth-like back sheet. Some use as many as nine inks with all kinds of well-known characters such as Disney, Sesame Street, Soccer teams, etc. Another gimmick they use is a wetness indicator. This is typically used for adult products but some baby diapers also use it.

Protective mattress pads are generally quilted and use large volumes of spun-bonded nonwoven fabrics as facing and backing materials. In this application, nonwoven fabrics have captured about half of the total volume and compete directly with woven cotton. Spunbonded polyester is often used as it is strong and retains its shape during laundering. Facing fabrics are generally 42-65 grams/meter² while backing fabrics are usually in the 15-20 grams/ meter² range.




We are engaged in this area for more than ten years, different kinds of nonwoven fabrics such as coating laminated or composited nonwoven fabrics
we are manufacture of all type of nonwoven fabric in india
any reuirement to contact me +91 8200595433
Dear sir,
I have one new idea for making of non woven fabric.
Dear Sir.
This is Eng.Taqwa Alzubi, from JERASH THE FIRST Company.
We are an American company that produces PPEs (Personal protective equipment) located in Amman.
We are looking for a fabric supplier, SMS, PP PE Laminated.
Our target GSM =20,25,30,35,40 , both blue & white colors.
Can you provide us with SMS, PP, or PE fabrics, GSM=20,25,30,35,40?
Wating for your promoting reply.
Regards.
Eng.Taqwa Alzubi
As a nonwoven fabric factory:
Www.cswf.cn,we are proud of what we are working.As a Chinese non woven fabric factory,we are proud of what we are working
Non Woven Fabrics is best for environment health parknonwoven.com also manufacturers and suppliers of the non woven products.
We focus on
www.jcppfabric.comnon woven geotextile,Our Non Woven Geotextiles are comprised of strong polypropylene or Polyester staple fibers.