Linen Fiber and Linen Fabrics from the Flax Plants
Cellulose, bast fibers from flax plants - one of the oldest known natural fibers
Linen fabric is made from the cellulose fibers that grow inside of the stalks of the flax plant, or Linum usitatissimum, one of the oldest cultivated plants in human history.
Textiles in a Linen weave texture, even when made of cotton, hemp, and other non-flax fibers, are also loosely referred to as “linen”. Such fabrics generally also have their own specific names, for example, fine cotton yarn in a linen-style weave is called Madapolam.
Flax/Linen Clothing
Linen fabric has many attractive properties and all of them are most easily appreciated when wearing linen clothing. Over the past 30 years, the end use of linen has changed dramatically. Approximately 70% of linen production in the 1990s was for apparel textiles, whereas in the 1970s only about 5% was used for fashion fabrics.
The main benefit of wearing linen clothes in hot weather is the coolness they provide. Thanks to the weave and linen fiber specifics linen fabric allow more airflow and its structure means it stays away from your skin allowing better airflow over your body. Linen is a “stiff” fabric and is less likely to cling to the skin; when it billows away, it quickly dries out and becomes cool again. Summer clothes made of linen possess high air permeability, which allows air to flow through the fabric easily and allows the body to breathe.
Linen is a “stiff” fabric and is less likely to cling to the skin; when it billows away, it quickly dries out and becomes cool again. Summer clothes made of linen possess high air permeability, which allows air to flow through the fabric easily and allows the body to breathe.
Next, to coolness and high absorbency, linen has one more very favorable property – good heat conductivity characteristics. Heat conductivity refers to the extent to which heat can be conveyed through the fabric. As linen quickly allows the heat to escape, it further improves cooling. It is claimed, that heat conductivity of linen is five times higher than wool and eighteen times higher than silk. One more thing – linen weave reflects heat better, too. This means linen blouse, linen dress or shirt has good “shading” properties as well and again – the wearer of linen clothing feels cooler.

The legacy of Flax/Linen
In the past, linen was also used for books (the only surviving example of which is the Liber Linteus). Due to its strength, in the Middle Ages linen was used for shields, gambesons, and bowstrings; in classical antiquity, it was used to make a type of body armor, referred to as a linothorax.
Flax/Linen Applications
Linen uses range across bed and bath fabrics (tablecloths, bath towels, dish towels, bed sheets); home and commercial furnishing items (wallpaper/wall coverings, upholstery, window treatments); apparel items (suits, dresses, skirts, shirts); and industrial products (luggage, canvases, sewing thread). It was once the preferred yarn for hand sewing the uppers of moccasin-style shoes (loafers) but has been replaced by synthetics.
Non-clothing application of Flax/Linen

Linen fabric is one of the preferred traditional supports for oil painting. In the United States, cotton is popularly used instead, as linen is many times more expensive there, restricting its use to professional painters. In Europe, however, linen is usually the only fabric support available in art shops; in the UK both are freely available with cotton being cheaper. Linen is preferred to cotton for its strength, durability and archival integrity.
Linen is also used extensively by artisan bakers. Known as a couche, the flax cloth is used to hold the dough into shape while in the final rise, just before baking. The couche is heavily dusted with flour which is rubbed into the pores of the fabric. Then the shaped dough is placed on the couche. The floured couche makes a “non-stick” surface to hold the dough. The ridges are formed in the couche to keep the dough from spreading.
Flax/Linen Source
Linen is bast fiber. Linen is a textile made from hairs of the flax plant. Linen fabric is made from the cellulose fibers that grow inside of the stalks of the flax plant, or Linum usitatissimum, one of the oldest cultivated plants in human history. Flax is an annual plant, which means it only lives for one growing season. It is thicker than cotton and linen fiber has variable lengths, most of which are very long. This contributes to strength, which contributes to longevity. Linen fabric lasts a very long time.
Linen is laborious to manufacture, but the fiber is very absorbent and garments made of linen are valued for their exceptional coolness and freshness in hot weather. Linen/Flax fibers vary in length from about 25 to 150 mm (1 to 6 inches) and average 12–16 micrometers in diameter. There are two varieties: shorter tow fibers used for coarser fabrics and longer line fibers used for finer fabrics. Flax fibers can usually be identified by their “nodes” which add to the flexibility and texture of the fabric. The cross-section of the linen fiber is made up of irregular polygonal shapes which contribute to the coarse texture of the fabric.
Physical properties of Flax/Linen fibers
- Colour – yellowish to gray
- Length – 18 to 30 inches
- Tensile strength – tenacity of 5.5 to 6.5 gms/den.
- Elongation at a break – 2.7 to 3.5 %
- Elastic recovery – not enough
- Specific gravity – 1.54
- Moisture regain – 10 to 12%
- Effect of heat – excellent resistance, a good conductor of heat
- Effect of sunlight – not affected
- Resiliency – very poor
- Lusture – brighter than cotton, slightly silky
- Abrasion resistance – moderate
Chemical properties of Flax/Linen Fibers
- Bleaching action: Flax (Linen) is made difficult to bleach than cotton, its huge amount of impurities, like pectin and gum.
- Effect of Acids: Flax not affected by weak acids but is damaged by concentrated acids.
- Effect of alkali: Flax has good resistance to alkaline solutions
- Effect of organic solvents: high Resistant
- Effect of insects: Flax is not attacked by moth, grubs or beetles.
- Effect of micro-orgasms: Attacked by fungi and bacteria, mild dew feed on linen fabrics
- Dyeability: Not good affinity to dyes. Direct and vat dyes are suitable for flax fiber.
The chemical composition of Flax/Linen Fibers
| Raw Flax% | Ratted Flax% | |
|---|---|---|
| Cellulose | 56.5 | 64.1 |
| Semi-cellulose | 15.4 | 16.7 |
| Pectin | 3.8 | 1.8 |
| Lignin | 2.5 | 2.0 |
| Fat & wax | 1.3 | 1.5 |
| Water-soluble | 10.5 | 3.9 |
| Moisture regain (Water) | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| Total | 100% | 100% |
Characteristics of Flax/Linen Fiber/Fabrics
- Clothes that made of linen is comfortable to Use: As the Linen fiber is a natural vegetable fiber it has a huge amount of Air Porosity holes. So, the air can go in and out while wearing these linen clothes and which make these clothes quite comfortable.
- Linen Fiber is stronger than Cotton: Another reason behind of the linen fiber popularity is – you will get the same comfort like Cotton in the Linen fiber but the strength of the Linen fiber is twice than the Cotton fiber. Maximum sportswear where the strength is a matter, there the Linen fiber made linen clothes is widely used.
- Hand Washable & Dry Cleanable: You can not only wash the clothes linen but also clean the lien clothes by drying. So, making linen clothes by using the linen fiber is a wise decision for the Textile Industry owner.
- Crisp feeling: If you touch the linen fiber, you will feel that it’s a simply crisp fiber which has distinctive outlook and feels.
- Tailors Well: One textile weavers or textile knitter can easily make the Linen fabric by using the flexible linen fiber and the tailors of the Garment Shop, even can easily make Dress and suits by using the Linen fabrics.
- Absorbent: The absorbency of Linen fiber is quite good and this is why linen can be dyed well.
- Dyes & Prints well: Along with the optimum efficiency in Dyeing, one can easily print the Linen cloth except for any kind of problems like print paste saturation, discolored surface etc.
- Lightweight To Heavyweight: Any kind of linen fabric or linen fibers are available on the market which can be achieved in any weight as per the Textile buyers’ requirement.
- No Static & Pilling problems: If any fabric produces the static electricity during wear, then nothing can be worst than that. People like to wear the fabric that is flexible and comfortable to wear. Linen is the perfect fabric in this regard which has no static electricity and pilling problems.
- Good Abrasion Resistant: As the linen fiber is good in strength, then it is supposed to have the properties like Good abrasion resistant
Performance summary of Flax/Linen in apparel fabrics
- AESTHETICS – Excellent
- LUSTER – High
- TEXTURE – Thick and thin
- HAND – Stiff
- DURABILITY – Good
- ABRASION resistance – Good
- TENACITY – Good
- ELONGATION – Low
- COMPORT – High
- Absorbency – High
- THERMAL retention – Good
- APPEARANCE retention – Poor
- RESILIENCY – Poor
- DIMENSIONAL stability – Adequate
- ELASTIC recovery – Low
- RECOMMENDED care – Dry clean or machine wash
Carbon Fibre – strong, stiff, & light weight fibres
Properties, process, history, and application of carbon fibres
Natural silk – sourcing, usage, and application
Animal protein fiber, its source, usage, properties, fabric care, and application
Fabric characteristics
Linen fabrics have a course, natural-looking texture, and a slight sheen. They’re available in various weights and weaves.
Positive qualities
Linen is strong, absorbent, draws heat away from the body, and can withstand high temperatures. It is also a smooth fiber that’s lint free.
Drawbacks
Linen tends to wrinkle easily unless treated with a special finish. It can also shrink and soften if Linen also has poor elasticity – it tends to stretch without recovering its shape.
Care requirements
Since linen fabrics can shrink or soften if laundered, dry-cleaning is usually recommended. Iron linen using a high temperature.
Yarn Measure norms
The standard measure of bulk linen yarn is the “lea”, which is the number of yards in a pound of linen divided by 300. For example, a yarn having a size of 1 lea will give 300 yards per pound.
The fine yarns used in handkerchiefs, etc. might be 40 lea, and give 40×300 = 12,000 yards per pound. This is a specific length, therefore, an indirect measurement of the fineness of the linen, i.e., the number of length units per unit mass. The symbol is NeL. The metric unit, Nm, is more commonly used in continental Europe. This is the number of 1,000 m lengths per kilogram. In China, the English Cotton system unit, NeC, is common. This is the number of 840-yard lengths in a pound.
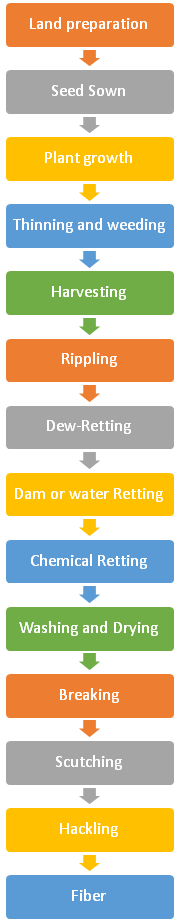
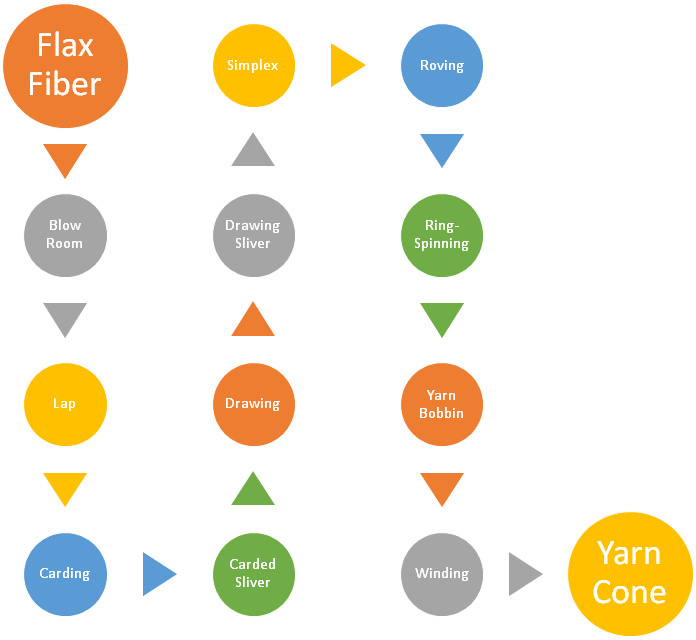
Flow Chart of Flax/Linen Yarn Production Process
Future of Flax/Linen Fiber
Currently, researchers are working on a cotton/flax blend to create new yarns which will improve the feel of denim during hot and humid weather.
Because of its strength when wet, Irish linen is a very popular wrap of pool/billiard cues, due to its absorption of sweat from hands. Paper made of linen can be very strong and crisp, which is why the United States and many other countries print their currency on paper made from 25% linen and 75% cotton.



Curtains behave an important role in decorating the room. In the antique times, it wasnt taken textile buying house. But those days are as soon as than, now people deem curtain designs every part of purposefully. Likewise, you need to shop for curtains and we have a curtain shop stuffy me. Keep reading this till the lie in wait to know anything approximately it.
Can you share the reference about the chemical composition of Flax/Linen Fibers? Tankyou in advance
Great article, and very informative. given it to all my lab staff.
i have a question, i get fabrics to do fibre identification on, like a viscose, cotton, linen blend, and would like to determine the composition % of each fibre, i can determine the viscose portion, but battling to determine the % difference between the cotton and linen. do you know how this is determined? any advice would be most helpful and appreciated..
best regards
William
check fibres with stiff hand feel, low elongation, are the linen fibres
Useful and informative.
Founded in 2001, Shenzhen, China, Profitex mainly engages in linen woven fabrics. With competitive price and outstanding products and services, we wish to establish long-term cooperation with our valuable clients.
Find more information, please visit our website
http://www.profitex-linen.com/.Ashok sir,
Excellent article I must say. Quite insightful.
I’m in process of starting a fashion label and focused on Linen apparel at the moment. I’m seeking your guidance in finding a good quality linen manufacturer or a reputed wholesaler I can reach out to.
I would greatly appreciate your time and response.
Kind regards,
Meher
UNABLE TO UNDERSTAND YOUR QUESTION. can U ELOBRATE