Denim Spinning Manufacturing Methods and Technologies
Denim fabrics are after all fabrics made with yarns of varying fibre properties and manufacturing processes. The article explains the process of spun yarn manufacturing in the context of denim fabrics manufacturing.
Blow Room
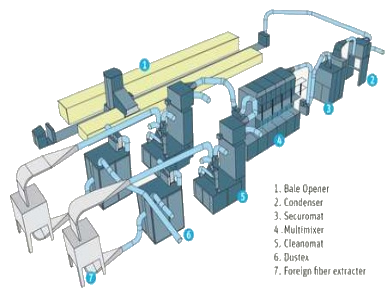 Thus, spinning denim yarn is really a large-scale business because of heavy yarns and fabrics. Denim comes in a wide range of types, including stretch denim, which is woven with 2 per cent Spandex, and poly denim, in which the cotton is blended with polyester to produce a lighter, easier to clean fabric. The modern Blow room line is with 4 to 5 beating points plus a micro-dust extractor and a very efficient automatic waste evacuation system.
Thus, spinning denim yarn is really a large-scale business because of heavy yarns and fabrics. Denim comes in a wide range of types, including stretch denim, which is woven with 2 per cent Spandex, and poly denim, in which the cotton is blended with polyester to produce a lighter, easier to clean fabric. The modern Blow room line is with 4 to 5 beating points plus a micro-dust extractor and a very efficient automatic waste evacuation system.
Cotton Used
Let us first start with the raw material. Cotton fibre specifications of important Indian varieties used in denim yarns. Various cotton is used, ranging from irrigated J-34 from North, hybrid Shankar-6 from Gujarat, windy V-797 of Saurashtra, lean season rescuer NHH-44 from the federation, quilty Bengal desi to cosmic bunny to name a few. Often recycled waste purchased comber noil of other mixings is also added. The percentage of trash in the mixing is for the mixing inclusive of usable waste and waste of other mixings added. When comber noil is added to the mixing, the yarn realization will be lower.
For every 10% comber noil addition in the mixing, the yarn realization will come down by 1%. Its obvious importance in Denim manufacture lies in the overall weight on the final cost represented by the cost of cotton. Because of heavy yarns and fabrics, if one can save 3 or 4% on cotton costs, the impact on the bottom line can be remarkable. This clean material has some residual trash in it not too different from the cotton used.
Naturally, there are shorter fibres. The yield will be approximately 50%, in other words from every 2 kgs of raw waste we get 1 kg of clean recycled cotton. This material is baled again and fed to the mix at the laydown. Normally 10% is used. A loss of some 0.5 to 1.0 cN/tex is then unavoidable, but with 10% it will be manageable. In general, a Modern Blow room line with 4 to 5 beating points with a micro-dust extractor and a very efficient automatic waste evacuation system will be adequate to ensure satisfactory opening and cleaning.
In the case of variations within regions, it is not uncommon to have fluctuation of colour from the bale and therefore blending becomes very critical if shade variations from lot to lot in the finished cloth are to be kept to a minimum. It is also possible to integrate a waste recycling line to recycle non-re-workable wastes from blow room line and cards to bring down the cotton cost. For denim yarns produced from open-end spinning systems, probably the most important characteristic of the sliver is its cleanliness with particular care to be given to dust removal.
Particularly in ring spun Denim yarn, a high incidence of nep in the yarn will cause uneven dye uptake during the warp yarn preparation. It is observed that modern blow room lines create neps, up to an increase of 100% over neps in raw cotton that will still allow the carding machine to be able to remove most of these objectionable faults.
Generally, blow room waste levels are as follows:
- Invisible loss: 1.5% on mixing fed
- Sweepings: 1.5% on mixing fed
The task of the Blowroom line is to:
- open the material into very fine tufts;
- eliminate most of the impurities;
- eliminate dust;
- provide a good blend.
Natural Indigo Blue Dye Origin Dying Procedures Technology and Dye Recipes for Denim Fabrics
Natural INDIGO Dye – THE KING OF NATURAL DYES
Denim Fabric Weaving – Manufacturing Process, Methods, and technologies
Manufacturing process of Denim Fabrics
And this has to be done:
- with very careful treatment of the raw material
- with maximum utilization of the raw material
- while assuring the optimum level of quality
The blow room installation as a sequence of machines
- Openers
- Cleaners
- Foreign part separators
- Mixers
- Separators
In processing the material, different types of machines are necessary, namely those suitable for opening, those for cleaning and those for blending. Different intensities of processing are also required because the tufts continually become smaller as they pass from stage to stage.
Accordingly, while a coarsely clothed cleaning assembly is ideal after the bale opener, for example, it is inappropriate at the end of the line. Therefore, there are no universal machines, and a blow room line is a sequence of different machines arranged in series and connected by transport ducts.
In its own position in the line, each machine gives an optimum performance – at any other position, it gives less than its optimum. Also, there may be advantages in different modes of transport, feeding, processing, cleaning and so on from one machine to another along the line. Finally, the assembly of a blow room line depends among other things on:
- the type of raw material;
- the characteristics of the raw material;
- waste content;
- dirt content;
- material throughput;
- the number of different origins of the material in a given blend.
Causes of excessive wastage extraction in blow room:
There are many reasons for which wastages are generated in the Blow room section. From a practical point of view, the following reasons are most important.
- The too-wide setting of grid bar in CL-P.
- Missing grid bar.
- High short fibre content.
- Improper cylinder speed in CVT-3.
- Incorrect gauge between feed rollers to 1st cylinder in CVT-3.
- Improper ambient condition.
- Wider winch angle setting in CVT-3.
Suggestive ways of wastage reduction and control in blow room:
- To reduce wastage, CVT-3 winch basic setting should be kept standard. The gauge usually beater to deflector blade is 1.5mm.
- Apply Cylinder speed, depend on fibre maturity and fibre length.
- Apply Feed roller to1st cylinder gauge in CVT-3 depend on fibre length.
- The opening and cleaning intensity depends, apart from other parameters, on the distance between the beater and feed roller, the speed of the beater and the grid bars setting.
- The Trutzschler’s waste sensor WASTECONTROL BR-WCT is attached to a Cleaner CLEANOMAT and optically measures good fibres in the waste and amount of suction for fibres.


