Textile composite materials
A class of advanced materials, which are reinforced with textile preforms for structural or load bearing applications
A composite textile material (also called a composition material or shortened to composite) is a material made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties that, when combined, produce a material with characteristics different from the individual components.
A Brief History of Textile Composites
Archaeologists say humans have been using composites for at least 4,000 to 6,000 years. In ancient Egypt, bricks made from mud and straw to encase and reinforce wooden structures such as forts and monuments. In parts of Asia, Europe, Africa and the Americas, indigenous cultures build structures from wattle (planks or strips of wood) and daub (a composite of mud or clay, straw, gravel, lime, hay, and other substances using a heat source for backing and drying from the sun).
Another advanced civilization, the Mongols, were also pioneers in the use of composites. Beginning around 1200 A.D., they began building high performance recurved reinforced bows out of wood, bone, and natural adhesive, wrapped with silk and pine resign (birch bark). These were far more powerful and accurate than simple wooden bows, helping Genghis Khan’s Mongolian Empire to spread across Asia.
The modern era of composites began in the 20th century with the invention of early plastics such as Bakelite and vinyl as well as engineered wood products like plywood. Another crucial composite, Fiberglas, was invented in 1935. It was far stronger than earlier composites, could be moulded and shaped, and was extremely lightweight and durable.
World War II hastened the invention of still more petroleum-derived composite materials, many of which are still in use today, including polyester. The 1960s saw the introduction of even more sophisticated composites, such as Kevlar and carbon fibre.
Definition of Composite Materials
A composite material (also called a composition material or shortened to composite) is a material made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties that, when combined, produce a material with characteristics different from the individual components. The individual components remain separate and distinct within the finished structure, differentiating composites from mixtures and solid solutions.
Loosely defined, a composite is a combination of two or more different materials that results in a superior (often stronger) product.
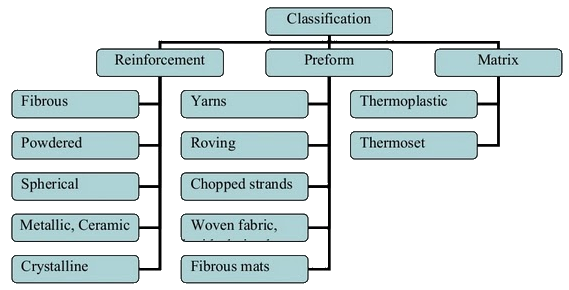
Classification of Composite Materials
How composite materials are classified? The composite materials are commonly classified based on matrix constituent. The major composite classes include Organic Matrix Composites (OMCs), Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs) and Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs). … These three types of matrixes produce three common types of composites.
Why we require composites
- Superior weight- specific strength and stiffness
- Broad flexibility in strength and stiffness tailoring
- High resistance to fatigue damage
- Chemical and corrosion resistance
- Very low thermal expansion
- Very high directional thermal conductivity
- Thermal and radar signature control
- Easy to make very complex geometries
- Can introduce significant material dumping


